Just before discussing the physical therapies of the torn meniscus. It’s quite better to have a sound knowledge of some of the important things that I am going to discuss below in the article because without these it will not be possible to have a complete therapy. So first and most important thing is to know.
Best Torn Meniscus Physical Therapies
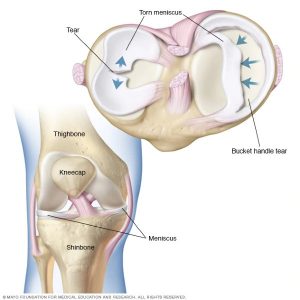
What a meniscus is?
Menisci (sg. meniscus) are basically two (medial and lateral) pads of fibrocartilaginous tissue that are present in the knee joint. These are the c shaped cartilage structures that are having the concave upper surface, which provides a great deep area for the articulation with the femur (Thighbone) and a lower flat surface that attaches to the tibia (shin bone).
What did the menisci do?
Menisci basically act as a pad of cushion dispersing the friction in the knee joint between the tibia and femur. They act as a shock absorber so less the force is transmitted to the lower bones and also a space-filler between the bones so they do not articulate directly as it will definitely limit the mobility of the joint. They also provide stability, lubrication, and proprioception through it’s insertional attachments.
How you can get the meniscal tear?
During the movement of the knee joint (particularly flexion) the menisci move outwards laterally and posteriorly. Lateral meniscus, with a range of mobility of 9.5mm posteriorly, is more mobile as compared to the medial. So owing to the less mobility and more fixity, the medial ligament is more prone to tears with a prevalence of 2:1. Any activity that involves;
- Wide range of movement
- Forceful twisting
- Increased pressure
- Excessive rotation of the knee joint
can cause a meniscal tear. Even simple kneeling, deep squatting, and lifting heavy weights can also result in tears.
Can YOU get a meniscal tear?
Yes, anyone can get a meniscal tear but you can have higher chances of getting it if you are;
- Athlete
- Obese (BMI > 30)
- Old age
- Footballer
- Tennis or basketball player
How can you confirm a meniscal tear?
Some of the signs and symptoms listed below may speak up for a torn meniscus but definitely there is more to go;
- Pain
- Swelling
- Stiffness (Locked knee)
- Unable to extend the knee fully
- Burning and popping sensation
But here are some of the tests that can confirm your suspicion.
- The presence of palpable joint line tenderness is the most sensitive clinical examination test for a meniscal tear. Simply flex the knee to about 90o and palpate the joint line using your thumb and index finger. Any tenderness (pain on touch) adds to the confirmation.
- Thessaly test: patient stands on the affected leg, rotating their body to twist the knee. This test is performed with the knee flexed first to 25o and then to 45o. Pain and giving way is diagnostic of the meniscal tear. (you may need to support the patient)
- McMurray’s test
- Apley’s grind test
The last two are not so reliable so they are not discussed here.
How to treat a meniscal tear?
Usually, a meniscal tear heals on its own in approximately 4-6 weeks if the joint is given rest and limited activity is performed. The only things that you can add up are;
- physical therapies
- anti-inflammatory drugs
- oral analgesics (pain relievers)
and if through these, the tear does not heal than the definitive treatment is the surgical repair.
Physical therapies
Physical therapy basically aims at;
- Reducing the stiffness
- Increasing the mobility
- Strengthening the thigh and calf muscles (so the less work is done by the knee joint and less pressure is transmitted to it.)
- Relieving the pain
- Fasten the recovery
Some of the best exercises that you can do at home easily are listed below which can provide you with the best results.
-
Mini-squats
These focus on strengthening your quadriceps.
Simply stand by a wall (hips, shoulders, and head touching the wall) slightly lower your body by bending your knees to almost 15o hold for almost 10 seconds in this position. Do about 2 sets of 20 repeats each.
-
Leg extensions
This is the easiest but highly effective exercise that you can perform anywhere in your house while sitting on a chair and watching TV.
Sit on a chair placing both feet on the floor. Flex your foot and raise the leg by fulling extending the knee joint. your leg should be straight and perpendicular to your body. Repeat 10 times for each leg. You can have two to three sets of 10 repeats each day.

-
Straight leg raises
Again, another so easy and effective exercise that you can do by simply lying on the floor. It strengthens the quadriceps (front muscles of the thigh) and stretches the hamstrings (back muscles of the thigh).
Lie on the floor with your left sole of the foot touching the floor and right leg extended completely. Now raise your right leg as much as your both knees come on the same level. Have 2 sets of 10 repeats for each leg.

-
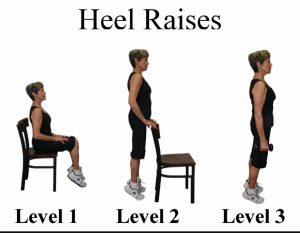
Standing heel raises
This exercise strengthens the calf muscles.
Simply stand straight with your hands resting on the back of chair or counter. Make your feet almost hip-width apart. Lift your heels off the ground and stand on your toes (level 2). Maintain this posture for almost 10 seconds. Have 2-3 sets of 10 repeats.
-
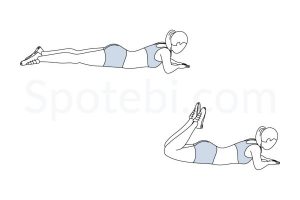
Hamstring curls
Lie straight on your stomach with legs fully extended and touching the ground.
Lift your head or make your forehead rest on your palms (your choice completely). Lift your right foot by bending the knee and try to touch your buttocks with your foot. Count for 20 and repeat it for 20 for each leg. You can have 2-3 sets each day.
All these exercises given above are really effective in the recovery after the meniscal tear. But sure, patience and persistence are needed.
Activities to avoid Physical Therapies
As in every case, there are also some DONT’S with the DO’S also.
- Jogging
- Bicycling
- Skipping
- Climbing upstairs
- Lifting heavyweights
Conclusion
A torn meniscus can be treated effectively by a multi-dimensional approach.



