Nowadays you must be hearing about knee replacement surgery so frequently. Because it is one of the most expensive and lifestyle changing surgery. It has a success rate of almost 90%. But PAIN is the hallmark of it that needs to be addressed most importantly.
Pain after Knee Replacement Surgery
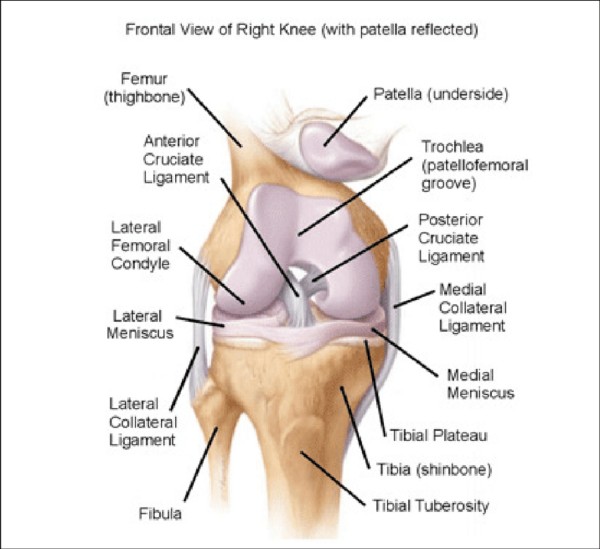
Anatomy of Knee joint
The knee joint is a complex synovial hinge joint. It is a combination of two tibiofemoral joints and one patellofemoral joint. Its structure makes it a highly unstable joint and stability is achieved by static (ligaments) and dynamic (muscles) stabilizers.
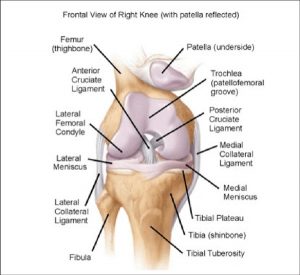
Movement at knee joint
Knee has a wide range of motion predominantly in the sagittal plane. It also has a mild degree of rotation. Hyperextension of 5o and flexion of about 135o. Recent studies through advanced imaging (MRI) have shown that it has also some sliding and rolling properties as well.
Why replace a knee?
As it is evident from the discussion above the knee joint is highly complex but as well as the most important joint in the body. Damage of this joint can completely make a person handicapped and affect daily activities to a great extent. So after hard tries finally the knee replacement surgery comes to play a significant role in the rehab of these patients.
Indications for the knee replacement surgery
Complete Joint destruction due to any of the following;
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Inflammatory arthritis
- Post-traumatic degenerative joint disease
- Osteonecrosis
- Severe pain
- Immobility and stiffness
contraindications for knee replacement surgery
some of the diseases are not associated with good outcomes of the surgery these include.
- diabetes
- hypertension
- coagulopathies
- peripheral arterial disease
- liver cancer
- renal failure
- chronic lung diseases
- endocrine disorders
more of the conditions that need to be addressed before the surgery include active knee sepsis, previously untreated or chronic osteomyelitis, active remote source of infection, absent extensor mechanism, and severe untreated or untreatable peripheral arterial disease.
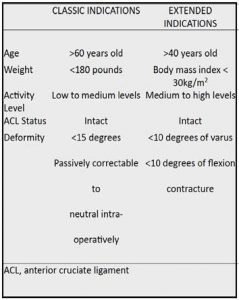
Criteria to select the patient for surgery
There are basically three key factors on the basis of which the patient is selected for knee replacement surgery;
- Patient age
- Radiographic evidence of severe osteoarthritis
- Clinical signs and symptoms
Knee replacement surgery
The knee joint is divided into three compartments.
- Medial tibiofemoral compartment
- Lateral tibiofemoral compartment
- Patellofemoral compartment
Most commonly medial compartment is affected. Females are more prone to it. So on the basis of this knee replacement is divided further into;
- Uni-compartmental replacement
When only one compartment is involved’
- Tri-compartmental / total knee replacement
When all of the three are involved then more extensive surgery is carried to replace all the destroyed parts. It is really difficult to restore the same motion in the TKR so the patients are not really much satisfied with it. There are three types of TKR used;
- Unconstrained
- Constrained non-hinge
- Constrained-hinge
Usually, unconstrained ones are preferred as there are more chances of loosening with the constrained one that will further lead to more pain.
What is actually done in knee replacement surgery?
Basically, in this procedure, the articulating surfaces of bones (tibia and femur) are replaced by metal and the menisci in between are replaced by tough polyethylene pads.
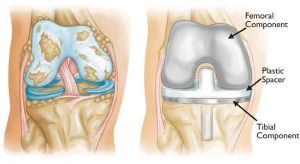
Causes of PAIN after knee replacement surgery
Pain, swelling, and stiffness after knee surgery are completely normal usually lasting for months. Mostly it takes a month for swelling to settle. Stiffness improves with physical therapy. It takes several months for the pain to get settle. But if the pain does not improve with time or does not settle after even several months it means some underlying complication has occurred;
Intraoperative complication
- Misplacement of implants (more pain and stiffness)
- Nerve or vessel injury
- Fracture
- Patellar tendon avulsion
- Malalignment
Postoperative complication
- Infection
- Stiffness
- Instability
- Osteolysis
- Component losing
- Dislocation
- Periprosthetic fractures
- Patellar mal-tracking
Steps were taken to minimize pain
- Weight reduction
Patients should encourage weight to lose before the operation as it reduces the complications and many comorbid.
- Regular exercise
Before and after surgery it is recommended so the stiffness of the joint can be reduced. Many rehabilitation centers are working on physical therapies after knee replacement.
- Analgesics
The use of pain-relieving medication is really important. Some settings are also using narcotics as the painkillers because pain is really discomforting for the patient.
- Anti-inflammatory
Definitively so much effective in reducing the inflammatory reaction which leads to marked decrease in redness and swelling of joints
- The long term walking aids
Even after the knee replacement for a long period of time approximately for one-year walking stick should b used as it transmits less load on the knee joint.
- Good diet
Good nutrient intake is important for fast recovery. As the food is the fuel to the body.
- Antibiotics
In the case of infection, broad-spectrum antibiotics should be started to combat infection.
- Knee Arthrodesis
It is done in complete failure of knee replacement surgery. The ideal position of fusion is 7o of valgus and 15o of flexion. Arthrodesis is performed using either a custom-made intramedullary nail or an extramedullary technique such as an external fixator.
- Revision knee replacement
This is the procedure which is indicated if any of the following has occurred;
- Severe infection of joint
- Loosening of implant
- Polyethylene induced osteolysis
- Peri-prosthetic fractures
- Malalignment
- Instability
- Patellar mal-tracking
Conclusion
The knee joint is really a precious joint. Look after your joint health because nothing can replace natural machinery.